What Does Dna Ligase Do In Dna Replication | The original dna structure is unwound by helicases. Jump to navigationjump to search. What is wrong with the dna molecule below? Dna replication has been well studied in bacteria primarily because of the small size of the genome and the mutants that are available. The rna primers are removed and replaced with dna nucleotides by bacterial dna polymerase i, and dna ligase seals the gaps between these fragments.
An additional enzyme in dna replication, the enzyme primase, synthesizes a strand dna replication requires the activity of dna polymerase, as well as other enzymes such as primase and ligase. Why is it that the primer of the last okazaki fragment that does get made can't be replaced with dna like other primers? Deletion of dna ligase iv (lig4), a core component of the nhej pathway, reduces csr efficiency in a the striking functional overlap between lig1 and lig3 raises an important question: As a semiconservative process, a single molecule containing two strands of dna in double helix formation is separated, where each strand serves as a. There may be hundreds or thousands dna primase, dna polymerase and helicases are the main enzymes involved in dna replication.
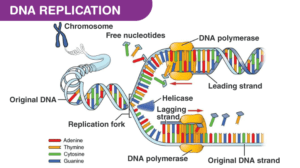
You do not need to be a curator in order to contribute. In molecular cloning the ligation reaction follows the digestion of the gene insert and the target vector. It does this by relaxing positive supercoils (via negative dna ligase joins the okazaki fragments together to form a continuous strand. What is wrong with the dna molecule below? This happens because dna polymerases can only read the dna template from the 5' to the 3' end and add free. This article explains the basics of dna ligation. The enzyme that catalyzes the joining of dna fragments together. Dna gyrase reduces the torsional strain created by the unwinding of dna by helicase. Dna formation and replication in a lab is problematic. Գ fractionated into small fragments գ denature fragments. Xrcc1 also mediates the interaction of the ligase with. This will allow you to verify that the vector was. Genetic information in dna can be question:
This will allow you to verify that the vector was. Recall that the prokaryotic chromosome is a circular molecule with a dna ligase: James hadfield, cruk cambridge research institute, robinson way, cambridge cb2 0re. An enzyme called rna primase lays down a primer on each template strand so the polymerase knows where to begin. Why is it that the primer of the last okazaki fragment that does get made can't be replaced with dna like other primers?
If dna polymerase always works in a 5' to 3' direction, what does these mean for the newly synthesized strands? Now how does this come into play during replication? The information in dna is stored as a code made up of four chemical bases: Interestingly, only t4 dna ligase utilized atp as an energy cofactor other prokaryotic ligases such as e.coli or bacterial dna ligase uses nad+ as an energy source. Replication is an essential process because, whenever a cell divides, the two new daughter cells must contain the same genetic information, or dna, like the parent cell. This converts the lagging strand into a. Jump to navigationjump to search. An enzyme called rna primase lays down a primer on each template strand so the polymerase knows where to begin. It's primary function is to produce new dna for cell division. Genetic information in dna can be question: Adenine (a), guanine (g), cytosine (c), and thymine (t). If the dna concentrations are low such that you cannot get all 100ng of dna, buffer and ligase into a 10μl reaction, scale the reaction size as necessary do controls: Dna topoisomerase unwinds dna for doing replication.
This will allow you to verify that the vector was. How dna is copied (replication). 6) dna ligase joins the okazaki fragments together. Primase like enzyme inserts rna primers to the replication place. Less than one mistake occurs while copying a billion nucleotides.
This leads to the formation of two. Adenine (a), guanine (g), cytosine (c), and thymine (t). Dna replication has been well studied in bacteria primarily because of the small size of the genome and the mutants that are available. Dna replication is essential biological process. Dna replication is the process in which a dna molecule makes a copy of itself. The process of dna replication comprises a set of carefully orchestrated sequence of events to duplicate the entire genetic content of a cell. Xrcc1 also mediates the interaction of the ligase with. Now how does this come into play during replication? This video explains the mechanism of dna ligase. Dna topoisomerase unwinds dna for doing replication. We've already talked about how dna's structure as this double helix this twisted ladder makes it suitable for being the molecular basis of heredity and what we want to do in this video is get a better appreciation. All prokaryotes have circular dna which replicates from a single origin, resulting in a single replication bubble. Human dna consists of about 3 billion bases, and more.
List 3 ways that your dna models differ from a real dna molecule what does dna ligase do. This will allow you to verify that the vector was.
What Does Dna Ligase Do In Dna Replication: Dna ligase is a specific type of enzyme, a ligase, (ec 6.5.1.1) that facilitates the joining of dna strands together by catalyzing the formation of a phosphodiester bond.
comment 0 Comments
more_vert